- Professional Employer Organization (PEO)
- Artículo
- Lectura de 6 minutos
- Last Updated: 10/09/2025
What Is a PEO? A Guide to Understanding Professional Employer Organizations
Worried About HR Issues?
We're Here To Help.
Obtenga una cotización gratis

Table of Contents
What exactly is a professional employer organization (PEO)? This guide breaks down the definition of a PEO company, its operational structure, reasons businesses partner with one, and the various PEO models available.
As a business owner juggling endless priorities, robust HR solutions and competitive benefits packages might seem like distant dreams. That's where understanding the power of a PEO could be the game-changer your business needs.
What Does PEO Stand For In HR?
PEO stands for "Professional Employer Organization."
What Is A PEO Company?
A PEO is a partner that helps you manage HR, payroll, benefits, risk management, and provides compliance support for businesses. This arrangement divides responsibilities between the employer and PEO through a service agreement.
Key advantages include:
- Streamlined HR tasks so you can focus on your core business. Research from Paychex found that 51% of leaders said the number one benefit of outsourcing HR administration was fewer mistakes.¹
- Access to enterprise-level benefits at affordable rates.
- Expert HR guidance for specific challenges.
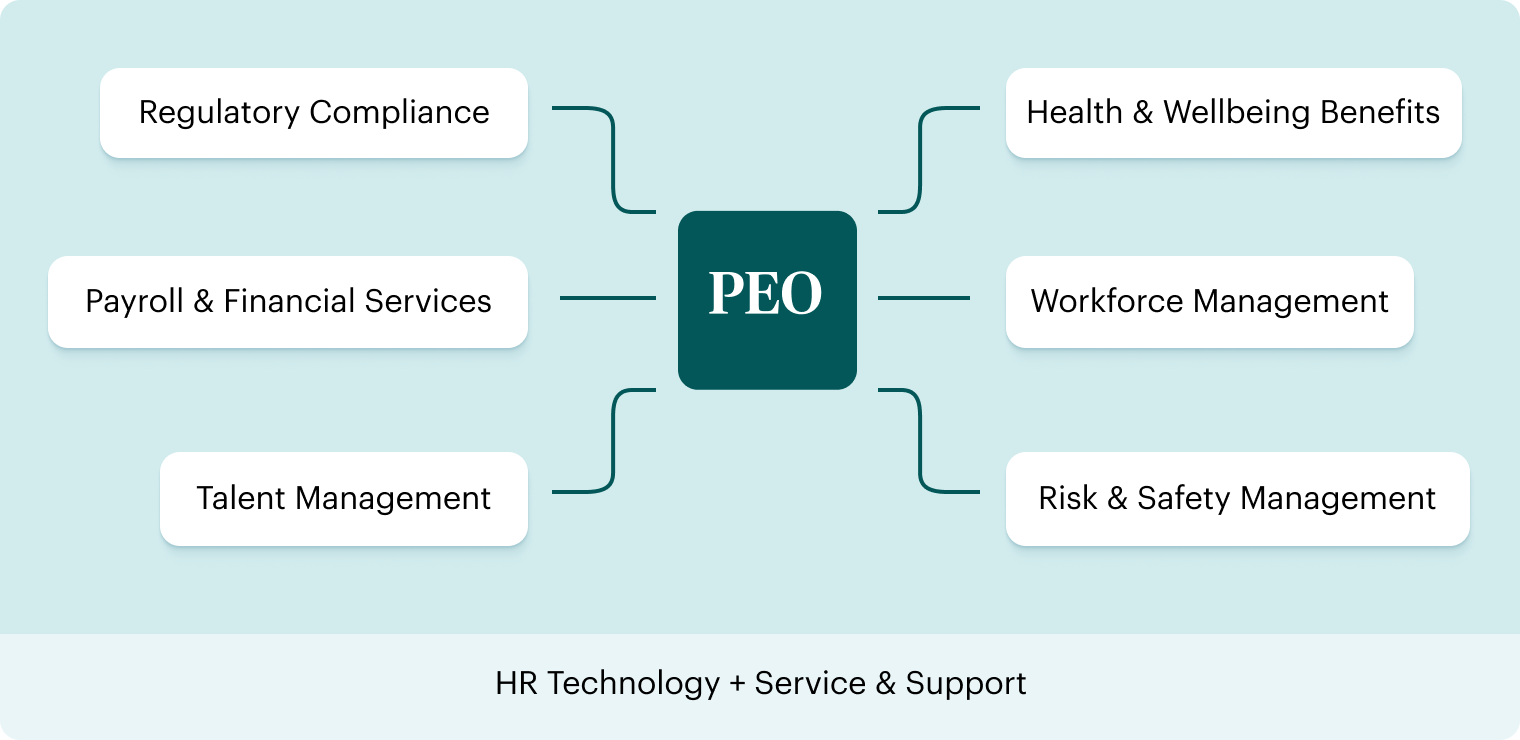
PEOs vs. In-House HR Models
When choosing between a professional employer organization (PEO) and an in-house HR model, businesses must weigh factors like cost, resource allocation, and strategic needs. Both approaches offer distinct benefits depending on the company's size, industry, and goals.
| Criteria | PEO (Professional Employer Organization) | In-House HR Model |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | PEOs charge a service fee but often reduce costs regarding group rates for benefits, SUTA, workers’ compensation coverage, and streamlined HR processes | Higher costs may come from time spent on HR tasks, understanding compliance requirements, recruiting, and software needs |
| Resource Allocation | PEOs help support payroll, taxes, benefits, and related compliance, freeing up internal resources | Internal teams manage all HR tasks, demanding more time and expertise |
| Compliance Management | PEOs help support compliance with employment laws, reducing regulatory risk | Businesses must stay up to date with regulations increasing compliance risk and workload |
| Employee Benefits | PEOs offer competitive benefits through pooled buying power, ideal for smaller businesses | Benefits are managed directly by the business often resulting in less favorable terms for small companies |
| Payroll Management | PEOs reduce administrative tasks, such as payroll processing, tax withholdings and filings. Many taxes are filed through the PEO federal ID number. | Businesses manage payroll and tax compliance internally or through software requiring more oversight |
| Business Control | PEOs engage in a co-employment administrative relationship with the client company | Businesses maintain full control over HR functions allowing for complete customization |
| Scalability | PEOs provide technology and services that scale with the client's business and workforce needs | Businesses must expand HR teams and systems as they grow increasing costs and resources needed |
| HR Expertise | PEOs provide expert guidance across HR areas like employee relations and safety | Internal teams rely on in-house expertise which can be costly to maintain |
| Strategic Focus | PEOs support HR admin tasks allowing leaders to focus more on business growth | Leadership is more involved in day-to-day HR which can divert focus from strategic initiatives |
How Does A PEO Work?
Engaging with a Professional Employer Organization (PEO) is a strategic move that can streamline your HR operations and support business growth. Here's how to begin:
- Assess Your Needs: Identify the HR challenges you're facing-whether it's compliance, payroll, benefits, or employee engagement-and determine which services a PEO company could help you manage more effectively.
- Research and Evaluate: Look for providers with strong industry experience, relevant accreditations (like ESAC or IRS certification), and a service model that aligns with your business goals.
- Have a Meeting: Schedule a consultation with a PEO sales rep to discuss your business needs, ask questions, and explore service options. This is a key step in understanding how the PEO can tailor its offerings to your organization.
- Get a Proposal: After the initial meeting, the PEO company will typically provide a detailed proposal outlining services, pricing, and implementation timelines. Review this carefully to ensure it meets your expectations.
- Prepare Internally: Align your internal team and systems for the transition. This may include gathering employee data, reviewing current HR processes, and designating a point person for the onboarding process.
- Begin Onboarding: Once you've signed the agreement, the PEO will guide you through onboarding-setting up payroll, benefits, compliance protocols, and employee access to HR tools.
If you need assistance navigating the PEO selection process, reach out to a Paychex representative who can help match your specific business needs with the right HR solutions.
What Doesn't a PEO company Do?
Unlike staffing companies that flood you with temporary workers, PEOs take a different approach. They don't recruit or hire employees for you — instead, they empower the team you've already built.
PEO companies do not:
- Supply labor to worksites. PEOs provide services and benefits to the employer and may also provide services directly to the client’s employees.
- Control your business or employees. PEOs provide access to HR advice and guidance to lean on when you need assistance.
- Replace your internal HR staff. PEOs supplement existing teams with specialized expertise in compliance, safety, benefits, and risk management.
PEO companies differ from other service models, such as:
- Staffing companies
- Managed payroll providers
- Administrative services only (ASO)
Why Do Companies Use a PEO? PEO Advantages
For employers already stretched thin on time and energy, partnering with a PEO unlocks valuable company resources that would otherwise be spent on administering payroll and other time-consuming tasks.
Businesses can expect many valuable PEO outcomes, including:
- Time Savings: Focus on core business while PEOs help with HR tasks.
- Cost Savings: Access group buying power for workers' comp and health insurance.
- Peace of Mind: Expert HR support throughout the employment lifecycle.
- Competitive Benefits: Fortune 500-level packages covering physical, mental, and financial wellness.
- Risk Management: In-depth HR assessments to minimize risk and maximize growth.
- Business Growth: NAPEO data shows that businesses that use a PEO grow two times faster and have employee turnover that is 12% lower.
- Recruiting Support: Assistance with hiring, onboarding, training, and retention strategies.
- Compliance Help: Navigate complex regulations with expert HR guidance.
- Employee Satisfaction: Competitive benefits boost morale and productivity.
- Technology Access: Advanced HR platforms with automation and self-service options.
How To Choose a PEO
When selecting a PEO, focus on finding the right mix of services, benefits, flexibility, stability, and reputation for your specific needs. Learn more about choosing a PEO.
Future Trends in PEO Services
With the business environment continuously transforming, PEOs are evolving to tackle emerging challenges and embrace technological innovations. Below are some key trends expected to shape the future of PEO services:
- AI-Powered HR Analytics: Real-time insights for data-driven decisions on hiring and retention.
- Personalized Engagement: Tailored wellness and development programs based on individual employee needs.
- Global Remote Support: Compliance management and benefits for distributed teams worldwide.
- Automated Compliance: Systems that track regulatory changes and help you reduce risks.
- Smart Learning Platforms: AI-driven training that personalizes skill development paths.
- Emerging Tech Integration: Blockchain security, VR training, and predictive analytics.
Enhanced Wellness Focus: Comprehensive mental health support and personalized wellness plans.
FAQs About PEOs
-
Do PEOs Provide Employee Benefits?
Do PEOs Provide Employee Benefits?
A company's employees may gain access to benefits typically available only to large companies when they work with a PEO. This can include health insurance, disability insurance, employee assistance and discount programs, 401(k) plan administration, and other benefits. Beyond these, PEOs may provide online access to employees’ reports, pay stubs, and W-2 forms to enable employee self-service, often leading to better engagement in the programs and the company culture.
Companies that work with a PEO usually experience lower group insurance costs since PEOs can negotiate rates with insurance companies with a larger employee count. PEOs may offer a lower state unemployment insurance (SUI) rate in certain states.
-
Who Is the Employer and Who Is Responsible for Employees?
Who Is the Employer and Who Is Responsible for Employees?
Organizations that enter a PEO relationship maintain control of their business. The PEO may assist with many employment-related aspects of a company, such as payroll, HR administration, employment-related taxes, and employee benefits. This support helps the organization to find more time to oversee its day-to-day business operations, encompassing employee hiring, performance management, leadership development, and accounting.
-
Is the Use of PEOs Growing?
Is the Use of PEOs Growing?
Seventy-eight percent of business leaders report it's extremely or highly likely that they will outsource HR administration in the year ahead.1 The top priority for outsourcing to a PEO was to help with HR management for employee relations, strategy, policies, and procedures.
Where does outsourcing to a PEO deliver the most value? Leaders rank these areas as most helpful to outsource:1
- HR management support
- Recruiting and onboarding
- Payroll processing
- 401(k) administration
- Benefits administration
- Assistance with managing employee performance
- Risk management/workers’ compensation
- Assistance with maintaining regulatory compliance
-
How Many Businesses Use a PEO?
How Many Businesses Use a PEO?
PEOs in the United States provide services to more than 200,000 small and mid-sized businesses, employing 4.5 million people.2
-
How Can a PEO Help You Control HR Costs?
How Can a PEO Help You Control HR Costs?
A PEO's economies of scale and buying power can help to lower certain employment costs and increase the bottom line. You may be able to maintain a simple in-house HR infrastructure or none at all by relying on the PEO, thereby reducing overhead. A PEO can assist with employer compliance and time savings by handling routine and redundant activities.
-
How Much Does a PEO Cost?
How Much Does a PEO Cost?
The cost of a PEO is determined by several factors, including the size of the business, which HR services will be outsourced, and the number and type of employees on the payroll. PEOs typically charge either a flat fee per employee or a percentage of the total payroll.
Suppose you have the choice of using either pricing model. In that case, you may wish to calculate the yearly expenses using both pricing models to evaluate expected PEO costs and determine which option makes the most financial sense for your business.
-
How Do PEOs Make Money?
How Do PEOs Make Money?
PEOs generally generate revenue through fees associated with their service agreement with their clients. The charges typically vary based on the total number of employees in the organization and the extent of services requested.
-
Are PEOs Accredited and Audited?
Are PEOs Accredited and Audited?
When researching PEOs, knowing how or if they are accredited and independently audited should be an essential part of your selection process. For example, Paychex PEO has a SOC 1 Type II certification focusing on outsourced services performed by service organizations relevant to a company's financial reporting. Paychex is accredited by the Employer Services Assurance Corporation (ESAC). ESAC is the nationally recognized financial assurance, standard-setting, and monitoring entity for the Professional Employer Organization (PEO) industry. Through its voluntary accreditation process, ESAC ensures that participating PEOs adhere to ethical, financial, and operational standards to promote high integrity and responsibility within the PEO industry. As a condition of continued accreditation, we must submit quarterly reports to ESAC, including financial statements and an independent Certified Public Accountant's verification of the timely and accurate payment of all payroll taxes, employee benefits contributions, and insurance premiums.
-
What Is a Staffing Agency?
What Is a Staffing Agency?
Staffing agencies generally find and place employees at a client organization for a fee. While A PEO may help with aspects of the hiring process (such as posting open positions on job boards, helping to write position descriptions, and applicant tracking), they are not responsible for hiring and placing employees for a client organization. Instead, a PEO will generally provide payroll, benefits, HR administration, and compliance monitoring services.
-
What Is Employee Leasing?
What Is Employee Leasing?
"Employee leasing" generally refers to a business arrangement in which a staffing agency supplies its employees to another business, typically for a specified period or project duration. Whether a PEO is considered a leasing company may depend on state-specific definitions and regulations.
-
What Are Some Potential Advantages of Working With a PEO?
What Are Some Potential Advantages of Working With a PEO?
PEO specialists bring a breadth of cross-industry expertise. They meet diverse challenges and use a comprehensive toolbox for effective problem-solving. This versatility can result in helpful employee- or HR-related resolutions.
Look for a PEO that prioritizes continuous training, helping to ensure specialists stay abreast of the latest employee relations and HR developments. This commitment places PEOs at the forefront, providing clients with up-to-date solutions and strategies.
Moreover, PEOs often provide digital technology platforms for employees to access essential documents, including pay stubs, W2s, and PTO balances. Additionally, PEOs can improve a company's benefits package, introducing valuable features like Flexible Spending Accounts (FSAs), Health Savings Accounts (HSAs), commuter benefits, and employee assistance programs (EAP), helping to enrich the overall employee experience.
-
What Are the Tax Implications of Working With a PEO?
What Are the Tax Implications of Working With a PEO?
Several PEOs handle payroll taxes on behalf of a client by using the PEO's tax ID for federal purposes and in states when it's allowed. Upon exiting the PEO arrangement, the shift occurs to pay taxes under the client's tax IDs, and certain wage base contribution caps will start over. This underscores the importance of strategically timing the exit from a PEO, making January 1st an ideal choice to ensure a smooth transition and compliance with tax obligations.
-
Does Working With a PEO Affect Company Culture?
Does Working With a PEO Affect Company Culture?
Working with a PEO won't inherently affect your organization's culture unless that aligns with your specific goals. Some PEOs may offer guidance and recommend strategies to shape your company's culture and brand, where this is part of your objectives. This can support your goal of employees perceiving your business in a manner that reflects your desired image both presently and in the future.
-
What Is a BPO?
What Is a BPO?
Business Process Outsourcing (BPO) involves delegating internal company practices to a third party covering payroll, IT management, website and social media management, benefits administration, and customer service. BPO companies assist businesses in saving costs by offering outsourced services as needed. For instance, small businesses may benefit from outsourcing IT management without the expense of hiring a full-time IT manager.
PEOs, unlike temp or staffing agencies, do not control hiring and firing decisions for their clients. PEOs offer a comprehensive range of employee and HR-related services, including payroll processing, tax handling, onboarding, benefits, and insurance.
While BPOs charge for specific services, PEOs often offer a more comprehensive bundled arrangement, offering multiple HR solutions for a combined fee.
-
Are There Different Types of PEOs?
Are There Different Types of PEOs?
PEOs do not supply labor to worksites or other staffing services, nor do they take over the hiring and management of your employees. PEOs are defined by their service agreements, so there can be some differences between PEOs depending on the extent to which they provide HR and employee relations support services for a business's existing workforce. In short, PEOs offer outsourced HR services.
Read more about the HR services offered by PEOs.
-
Will I Lose Control of My Business if I Work With a PEO?
Will I Lose Control of My Business if I Work With a PEO?
No. PEOs provide advanced HR tools, compliance support, and employee self-service features while allowing you to retain control over key business and personnel decisions.
-
Do PEOs Take Over Hiring and Firing Decisions?
Do PEOs Take Over Hiring and Firing Decisions?
No. You remain in charge of hiring, promotions, and terminations. PEOs assist with administrative tasks, allowing you to focus on these essential decisions.
-
Do PEOs Actually Save Businesses Money?
Do PEOs Actually Save Businesses Money?
Yes. PEOs can save businesses money by streamlining HR processes and offering competitive benefits, reducing costs and compliance risks.
-
Do PEO Certifications Matter?
Do PEO Certifications Matter?
Yes. Accredited PEOs, like Paychex HR PEO, meet high standards of ethical, operational, and financial reliability through organizations such as ESAC.
-
Will a PEO Limit My Benefit Options?
Will a PEO Limit My Benefit Options?
No. PEOs can offer more comprehensive and competitive benefits through collective buying power, including medical, dental, vision, life insurance, retirement plans, disability benefits, voluntary benefits, employee assistance programs (EAP), and other perks.
-
Will a PEO Replace My HR Team?
Will a PEO Replace My HR Team?
No. PEOs can enhance your HR team's efficiency by helping to support administrative burdens, allowing your HR staff to focus on employee engagement and development.
-
Are All PEOs the Same?
Are All PEOs the Same?
No. Not all PEOs are alike. Paychex PEO offers customized solutions, specialized support teams, and transparent billing, tailored to meet your specific business needs.
-
What Types of Companies Use and Benefit From PEOs?
What Types of Companies Use and Benefit From PEOs?
Any business can find value in a PEO relationship. The PEO industry’s 208,000 clients represent 17 percent of all employers with 10 to 99 employees.1 2
PEO clients include various types of businesses from various industries, including professional services firms, skilled trades companies, and high-tech organizations.
-
What's the Difference Between a PEO and HR Software?
What's the Difference Between a PEO and HR Software?
PEOs provide full-service HR outsourcing — assisting with payroll, benefits, training, and compliance guidance. HR software simply gives you a platform to manage these tasks yourself.
-
What's the Difference Between a PEO vs. Payroll Company?
What's the Difference Between a PEO vs. Payroll Company?
Payroll companies help you run payroll and calculate taxes, but you remain responsible for all obligations. PEOs take on payroll processing responsibilities, handle tax filing and remittance, and provide comprehensive support including compliance, workplace safety, workers' compensation, and HR administration.
1 2024 Priorities for Business Leaders, Paychex
Professional employer organization (PEO) services provided by Paychex Business Solutions, LLC (Florida employee leasing license GL7), Oasis Outsourcing, LLC (Florida employee leasing license GL42), and their affiliates, which are licensed or registered to provide PEO services where required by law.
Get Started With Paychex PEO Services
Paychex brings HR expertise to help businesses like yours access comprehensive PEO solutions that drive growth, reduce costs, and simplify operations. Our dedicated team works with you to create a customized PEO package that fits your unique needs and budget.
Tags